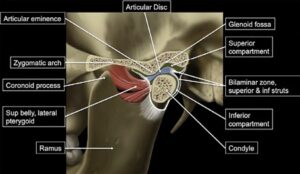
TMJ Internal Derangements https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/tmj-internal-derangements/#:~:text=It%20is%20commonly%20accepted%20that,fossa%20up%20the%20articular%20eminence. “Normal TMJ Anatomy2
As indicated by its name, the temporomandibular joint is the articulation between the mandibular condyle and the temporal bone fossa. These bones are buffered by a biconcave disc of fibrocartilage that is best thought of by its boundary attachments:
The lateral disc is anchored to the mandibular condyle via collateral ligaments, but is also integrated into the joint capsule itself. These ligaments serve to stabilize the disc in the joint.
The posterior disc is connected to the highly vascularized and innervated retrodiscal tissues, which connect to both the condyle and the temporalis bone. The retrodiscal tissues are also connected to the discomalleolar ligament,3 which originates in the middle ear. The retrodiscal tissue is passive in the closed position, but will limit the motion of the disc during maximum opening.
The anterior disc has connection with the joint capsule and the superior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle. The superior portion of the lateral pterygoid appears to contract during closing, stabilizing the disc during chewing.
The joint is innervated by the auriculotemporal and masseteric nerves, which are branches of V3”
The figure illustrates the different components of the temporomandibular joint. Contributed by Bruno Bordoni, PhD5
Fig 1: “Normal TMJ Function
It is commonly accepted that the temporomandibular joint has both rotational movement and translational movement, making it a ginglymoarthroidial joint. The mandibular condyle will rotate on the inferior surface of the disc and the superior surface of the disc will slide from the fossa up the articular eminence. Right and left lateral movements primarily involve translational movements by the contralateral joint (e.g. a left lateral movement involves translation of the right condyle). The complex nature of all mandibular movements is beyond the scope of this paper, but these basic movements can be demonstrated in any clinical setting”
… Over time, the disc may become abraded by the condyle, especially if the condyle has a more flattened architecture. Ongoing abrasion of the disc may lead to its perforation, resulting in continued popping with a grinding sound or “crepitus”* and worsening of the condition.”
Svenska: ”Med tiden kan skivan bli slipad av kondylen, särskilt om kondylen har en mer tillplattad arkitektur. Pågående nötning av skivan kan leda till dess perforering, vilket resulterar i fortsatt poppning med ett slipande ljud eller ”crepitus”* och försämring av tillståndet.
* Crepitus är rasande, sprakande eller knäppande ljud och förnimmelser som upplevs under huden och lederna eller en sprakande känsla på grund av närvaron av luft i den subkutana vävnaden .
Ljudet kan skapas när två ojämna ytor i en organisms kropp kommer i kontakt – till exempel vid artros eller ledgångsreumatism när brosket runt leder eroderar och ytorna i leden maler mot varandra, eller när de två frakturerade ytorna på lederna brutna ben gnuggar ihop. Crepitus är ett vanligt tecken på benfraktur .
Crepitus kan lätt skapas och observeras genom att utöva en liten mängd kraft på en led och på så sätt ” spricka den ”. Detta orsakas av att det bildas bubblor av kväve i ledvätskan som spricker. Nästan varje led i kroppen kan ”sprickas” på detta sätt, men de leder som kräver minst ansträngning inkluderar hallux , knogar och nackleder.
I mjuka vävnader kan crepitus bildas när gas förs in i ett område där det normalt inte finns.
Termen kan också användas för att beskriva de ljud som produceras av lung tillstånd såsom interstitiell lungsjukdom -Dessa också kallas ” rassel ”. Crepitus är ofta tillräckligt hög för att höras av det mänskliga örat , även om ett stetoskop kan behövas för att upptäcka fall orsakade av luftvägssjukdomar .
I tider av dålig kirurgisk praxis involverade postoperativa komplikationer anaerob infektion av Clostridium perfringens- stammar , vilket kan orsaka gasbrand i vävnader , vilket också ger upphov till crepitus. https://hmn.wiki/sv/Crepitus
Tinnitus, TMJ and bruxism https://www.miracle-ear.com/hearing-diseases/tinnitus-ringing-ears/tinnitus-tmj-bruxism
”Can TMJ cause tinnitus in one ear? Yes, tinnitus caused by TMJ and bruxism can also occur in just one ear. In fact, in these cases the tinnitus may be mainly present on the same side of the affected joint. Sometimes by clenching the jaw the patient can perceive a variation in the timbre and intensity of the tinnitus.”
Tinnitus is an auditory disorder that manifests itself in intermittent sounds like ringing in the ears. It can also be triggered by non-auditory incidents occuring in the head, neck and often the jaw. This relationship is rooted in the development of the middle ear with the trigeminal system of the jaw.
Tinnitus consists of the sensation of perceiving a sound that is not objectively present. Since tinnitus generally concerns ear structures, it is included in ear pathologies and the specialist mainly involved is the Otorhinolaryngologist. In many cases, however, no ear disease is found in the patient who reports it.
The connection between teeth, jaw and tinnitus may seem strange but it is extremely common. The central node is in the temporomandibular joint. One of the consequences of TMJ disorders can be tinnitus. The onset of tinnitus, although usually related to ear pathologies, can also be determined by non-otological factors starting from head and neck areas and, in particular, from the jaw and the temporomandibular joint. There are numerous findings of the frequent association between tinnitus and jaw problems.
Temporomandibular disorders (TMDs), such as temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ) and bruxism (a problem in which you unconsciously grind or clench your teeth), are the main cause of tinnitus in people with dental problems. Studies have shown that the auditory symptoms experienced in TMJ and bruxism patients are the result of the reciprocal influence between the temporomandibular joint and the auditory system
Can TMJ and bruxism worsen tinnitus? Given the reciprocal influence between the temporomandibular joint and the auditory system, it is possible for TMJ and bruxism to exacerbate existing symptoms of tinnitus. Ringing in the ears and other tinnitus sounds may intensify or be relieved by opening the jaw.
Can TMJ cause tinnitus in one ear?
Yes, tinnitus caused by TMJ and bruxism can also occur in just one ear. In fact, in these cases the tinnitus may be mainly present on the same side of the affected joint. Sometimes by clenching the jaw the patient can perceive a variation in the timbre and intensity of the tinnitus.
What does TMJ tinnitus sound like?
Tinnitus caused by TMJ and bruxism does not generate different sounds from other subjective tinnitus, so it typically sounds like a ringing, hissing, clicking or buzzing sound in the ear.
Can tinnitus from TMJ be fixed?
TMJ tinnitus is treated using common TMJ treatment protocol explained in previous post. Physical therapy, Night guards, ultrasound, Low level Laser Therapy(LLLT) and TMJ surgery are some treatment modalities for TMJ disorder that help fix TMJ tinnitus.
What is TMJ Tinnitus?
https://museumdental.com/can-tmj-cause-tinnitus/
Temporomandibular joint tinnitus is when you have noise in your ears caused by TMJ disorder. TMJ tinnitus usually resolve with the treatment of your TMJ disorder. Headache and ringing in the ears are common symptoms of TMJ dysfunction. To know if your tinnitus is caused by TMJ, changing the position of your jaw will more likely change the volume or pitch of your ear sound.
Can TMJ Cause Tinnitus?
The short answer to this question is, yes! TMJ can cause tinnitus. The TMJ is located just in front of the ear and share some nerve supply with ear. Inflammation and pain in the TMJ may alter the ear structure and the hearing perception causing abnormal sound hearing that does not exist. TMJ disc dysfunction may also cause clicking or crunchy sound that you and other people around you can hear.
An interesting fact is that ear ringing may be the only TMJ symptom you have. The good news is that TMJ tinnitus is treatable and will go away following proper TMJ treatment. However, studies found that patients with TMJ disorders are 3 times more likely to have ear ringing. On the other hand, people with TMJ headache are 6 times more likely to experience tinnitus.
How TMJ Tinnitus Treated?
As mentioned earlier, tinnitus is not a disease by itself. It is a symptom of a disease. Treatment of the underlying condition will fix the tinnitus problem. TMJ tinnitus is treated using common TMJ treatment protocol explained in previous post. Physical therapy, Night guards, ultrasound, Low level Laser Therapy(LLLT) and TMJ surgery are some treatment modalities for TMJ disorder that help fix TMJ tinnitus.